How to operate a drone is a question many aspiring pilots ask. This guide delves into the intricacies of safely and effectively controlling unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), from pre-flight checks and navigation to capturing stunning aerial footage and adhering to legal regulations. We’ll cover essential controls, flight modes, camera operation, maintenance, and troubleshooting, ensuring you’re well-equipped to take to the skies responsibly.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and mastering basic maneuvers. Learning the fundamentals is key, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced flight techniques. Ultimately, safe and effective drone operation comes down to practice and a solid understanding of the principles involved.
Understanding drone operation involves mastering both technical skills and a strong sense of responsibility. This guide aims to provide a balanced approach, blending practical instructions with a focus on safety and ethical considerations, equipping you with the knowledge to become a confident and responsible drone pilot.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight checklist is crucial for ensuring safe and successful drone operation. This involves inspecting key components, verifying environmental conditions, and understanding emergency protocols. Neglecting this step can lead to accidents or equipment damage.
Pre-Flight Inspection and Checklist
A comprehensive pre-flight inspection ensures the drone’s airworthiness. This includes checking the battery level, propeller condition, and GPS signal strength. A detailed checklist helps maintain consistency and minimizes the risk of overlooking critical steps.
| Item | Check | Action | Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| Battery Level | Check battery indicator lights and voltage | Charge if necessary; replace if faulty | |
| Propeller Integrity | Inspect for cracks, chips, or damage | Replace damaged propellers | |
| GPS Signal Strength | Observe the GPS indicator on the controller | Ensure a strong signal before takeoff; find a location with better reception if needed | |
| Gimbal Calibration | Check gimbal movement and stability | Recalibrate if necessary | |
| Controller Connection | Verify connection to the drone | Reconnect if necessary | |
| Flight Environment | Assess wind speed, obstacles, and airspace restrictions | Postpone flight if conditions are unsafe |
Emergency Procedures
Knowing how to react in emergency situations is paramount. This section Artikels procedures for common scenarios, emphasizing quick thinking and safe recovery.
- Loss of Signal: Immediately initiate Return-to-Home (RTH) function if available. If RTH fails, attempt to manually control the drone back to the pilot, prioritizing a safe landing area.
- Low Battery: Initiate RTH immediately. Land the drone as quickly and safely as possible in a suitable area.
- Unexpected Malfunction: Attempt to safely land the drone. If unable to regain control, prioritize the safety of people and property. Contact manufacturer support for troubleshooting and potential repair.
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation
Mastering the drone’s controls is fundamental to safe and effective operation. This section details the functions of control sticks and buttons, different flight modes, and core flight concepts.
Drone Control Stick and Button Functions
Understanding each control’s function is key to precise maneuvering. Improper use can lead to loss of control or accidents.
- Left Stick (Yaw and Throttle): The left stick controls the drone’s yaw (rotation) and throttle (altitude). Pushing the stick forward increases altitude; pulling it back decreases altitude. Rotating the stick left or right rotates the drone.
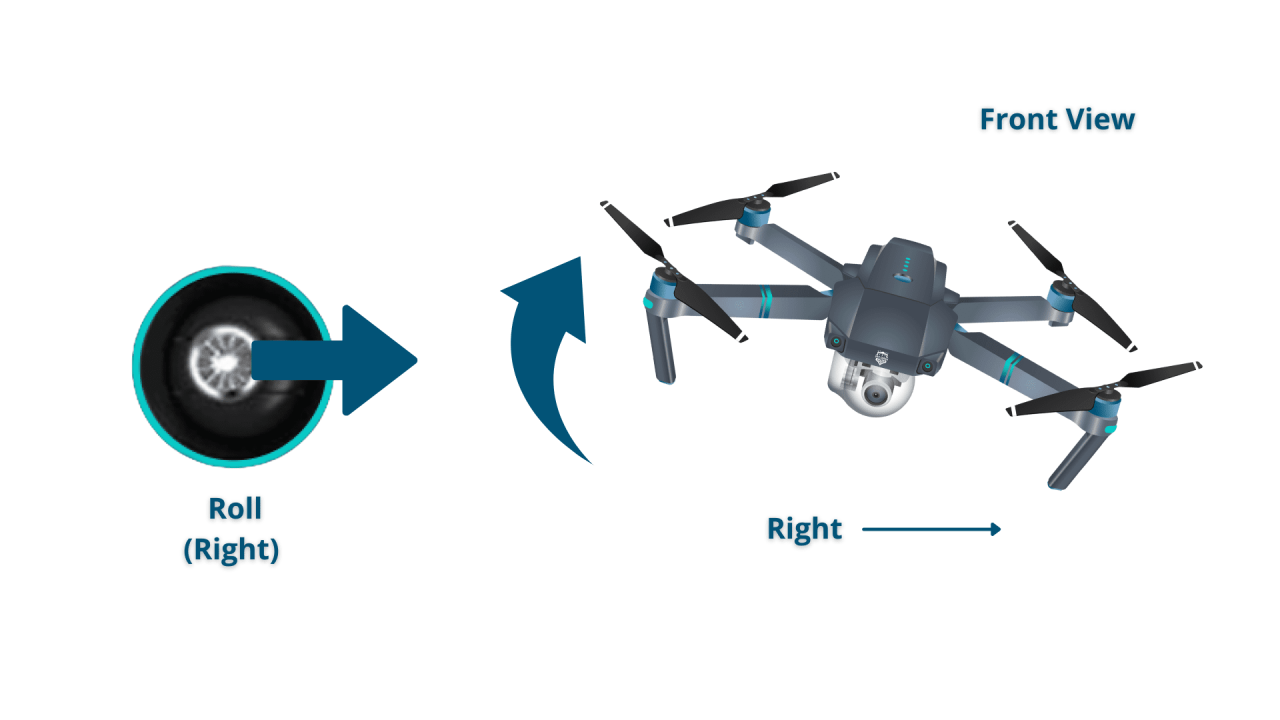
- Right Stick (Pitch and Roll): The right stick controls pitch (forward/backward tilt) and roll (left/right tilt). Pushing the stick forward moves the drone forward; pulling it back moves it backward. Pushing the stick left or right tilts the drone laterally.
- Return-to-Home (RTH) Button: Initiates an automated return to the home point (takeoff location).
- Emergency Stop Button: Immediately cuts power to the motors, resulting in an uncontrolled descent.
Flight Modes and Applications
Different flight modes offer varying levels of control and stability, adapting to different situations and pilot skill levels.
- Altitude Hold: Maintains a consistent altitude, simplifying hovering and reducing the need for constant throttle adjustments.
- GPS Mode: Uses GPS signals for precise positioning and stability, enabling features like RTH and waypoint navigation.
- Attitude Mode (or Rate Mode): Provides direct control over the drone’s attitude (orientation), allowing for more dynamic maneuvers but requiring more skill.
Understanding Yaw, Pitch, Roll, and Throttle
These four elements define the drone’s movement in three-dimensional space. Understanding their interplay is crucial for controlled flight.
Imagine a cube representing the drone. Yaw is rotation around the vertical axis (spinning the cube). Pitch is movement around the horizontal axis (tilting the cube forward or backward). Roll is movement around the lateral axis (tilting the cube left or right). Throttle controls the altitude (moving the cube up or down).
Taking Off, Flying, and Landing the Drone
Safe takeoff, flight, and landing procedures are essential for preventing accidents and protecting the drone. This section details the steps involved, emphasizing smooth and controlled maneuvers.
Safe Takeoff Procedures, How to operate a drone
Before takeoff, perform all pre-flight checks. Ensure a clear and open space free of obstacles. Begin the takeoff process smoothly, avoiding sudden movements.
- Power on the drone and controller.
- Wait for GPS signal acquisition (if applicable).
- Calibrate the compass (if necessary).
- Slowly and steadily increase throttle to lift the drone.
Smooth and Controlled Flight Maneuvers
Smooth and controlled maneuvers are key to safe drone operation. Avoid sudden movements or abrupt changes in direction.
- Hovering: Maintain a stable position in the air by making small adjustments to the control sticks.
- Turning: Use the left stick to smoothly rotate the drone. Avoid sharp turns, especially at higher altitudes.
- Ascending/Descending: Gradually increase or decrease throttle to ascend or descend. Avoid sudden changes in altitude.
Safe Landing Procedures
Landing requires careful attention to detail. Select a level, clear area free of obstacles. Approach the landing area slowly and smoothly.
- Slowly reduce throttle to descend.
- Maintain a steady descent rate.
- Gently lower the drone to the ground.
- Power off the drone and controller.
Drone Camera Operation and Video/Photo Capture
Many drones are equipped with high-quality cameras capable of capturing stunning aerial footage. Understanding camera settings and composition techniques is crucial for achieving optimal results.
Camera Settings and Features
Familiarize yourself with your drone’s camera settings to achieve the desired image quality. These settings can significantly impact the final output.
- Resolution: Determines the image size and quality (e.g., 4K, 1080p).
- ISO: Controls the camera’s sensitivity to light (higher ISO for low-light conditions, but can introduce noise).
- Shutter Speed: Affects motion blur (faster shutter speeds freeze motion, slower speeds create motion blur).
- Aperture: Controls the amount of light entering the camera (wider aperture for shallower depth of field).
Adjusting Camera Settings for Optimal Image Quality
Adjusting camera settings based on lighting conditions is crucial for capturing high-quality images and videos.
- Bright Sunlight: Use a lower ISO and faster shutter speed to avoid overexposure.
- Low Light: Use a higher ISO and slower shutter speed, but be mindful of potential noise.
- Overcast Conditions: Adjust settings based on the amount of ambient light. A slightly higher ISO may be necessary.
Composing Shots and Capturing High-Quality Media
Composition is key to creating compelling aerial photography and videography. Consider the rule of thirds, leading lines, and other compositional techniques to enhance your shots.
- Rule of Thirds: Place key elements off-center to create a more visually appealing image.
- Leading Lines: Use lines to guide the viewer’s eye through the image.
- Symmetry and Patterns: Capture symmetrical scenes or repeating patterns for visually interesting shots.
Post-Flight Procedures and Maintenance
Proper post-flight procedures and regular maintenance extend the lifespan of your drone and ensure its continued safe operation. This includes powering down the drone correctly and performing basic cleaning and inspections.
Powering Down and Safe Storage
Always power down the drone and controller correctly to prevent damage and ensure safety.
- Power off the controller first.
- Power off the drone.
- Store the drone in a safe, dry place away from extreme temperatures.
- Store the batteries separately and charge them only in a well-ventilated area.
Basic Drone Maintenance
Regular cleaning and inspection are vital for maintaining your drone’s performance and longevity.
- Cleaning Propellers: Gently clean propellers with a soft cloth to remove dirt and debris.
- Inspecting for Damage: Regularly check for cracks, scratches, or other damage to the drone’s body, propellers, and other components.
- Sensor Cleaning: Gently clean any sensors with a soft brush or compressed air.
Calibrating Sensors and Updating Firmware
Regular calibration and firmware updates are crucial for optimal performance and safety. Check your drone’s manual for specific instructions.
- Sensor Calibration: Calibrate the compass, IMU, and other sensors as needed to ensure accurate readings.
- Firmware Updates: Regularly check for and install firmware updates to benefit from bug fixes, performance improvements, and new features.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Operating a drone responsibly involves understanding and adhering to local laws and regulations, as well as ethical considerations regarding privacy and airspace safety. This section summarizes key legal and ethical guidelines.
Legal Regulations Governing Drone Operation
Drone regulations vary by region. It’s crucial to research and comply with all applicable laws and regulations before flying.
| Region | Registration Requirements | Airspace Restrictions | Other Regulations |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | Registration may be required depending on drone weight and use. | Restrictions near airports and other sensitive areas. | Rules regarding privacy and flight over people. |
| European Union | Registration and licensing may be required depending on drone class and use. | Stricter airspace restrictions compared to the US. | Regulations regarding data privacy and operational safety. |
| [Add other regions] | [Add registration requirements] | [Add airspace restrictions] | [Add other regulations] |
Ethical Considerations for Responsible Drone Use

Ethical considerations are crucial for responsible drone operation. Prioritize safety, respect privacy, and avoid any actions that could endanger others or cause harm.
| Ethical Consideration | Best Practice |
|---|---|
| Privacy | Avoid flying over private property without permission. Do not record individuals without their consent. |
| Airspace Safety | Always be aware of surrounding airspace and avoid flying near airports, helicopters, or other aircraft. |
| Responsible Use | Respect wildlife and avoid disturbing natural habitats. Fly only in designated areas when possible. |
Troubleshooting Common Drone Issues
Even with careful operation, drone malfunctions can occur. This section Artikels common problems, their causes, and troubleshooting steps to help resolve issues efficiently.
Common Drone Problems and Causes

Understanding common drone problems and their causes is crucial for effective troubleshooting.
- Low Battery Warnings: Low battery level, battery damage, excessive power consumption.
- GPS Signal Loss: Obstructions (buildings, trees), weak signal, GPS module malfunction.
- Unexpected Behavior: Software glitches, hardware malfunctions, interference.
- Propeller Failure: Damaged or loose propellers, motor malfunction.
- Controller Disconnection: Weak signal, interference, controller battery issues.
Troubleshooting Steps for Resolving Drone Malfunctions
Systematic troubleshooting can quickly identify and resolve most drone issues.
- Check Battery Levels: Ensure the drone and controller batteries are sufficiently charged.
- Check GPS Signal: Move to a location with a clear view of the sky and strong GPS signal.
- Restart Drone and Controller: Power cycle both devices to resolve minor software glitches.
- Inspect for Physical Damage: Carefully examine the drone for any physical damage to propellers, motors, or other components.
- Check for Software Updates: Ensure the drone’s firmware is up-to-date.
- Contact Manufacturer Support: If the problem persists, contact the manufacturer’s support for further assistance.
Troubleshooting Flowchart
A systematic approach to troubleshooting ensures efficient problem resolution. Start by checking the most common issues first and progressively investigate more complex problems.
Start -> Check Battery -> Check GPS Signal -> Restart Devices -> Inspect for Damage -> Check for Updates -> Contact Support -> End
Mastering the art of drone operation requires practice and a commitment to safety. By diligently following pre-flight procedures, understanding drone controls, and respecting legal and ethical guidelines, you can unlock the exciting possibilities of aerial photography and videography while ensuring responsible operation. Remember, continued learning and practice are key to becoming a proficient and responsible drone pilot.
Key Questions Answered: How To Operate A Drone
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with GPS and automated features are ideal for beginners. Look for models with good stability and ease-of-use features.
How often should I calibrate my drone?
Calibrate your drone’s sensors before each flight and as needed, especially after crashes or impacts. Refer to your drone’s manual for specific instructions.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires a good grasp of safety regulations and proper procedures. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques, check out this helpful resource on how to operate a drone and enhance your skills. This will ensure you’re confident and prepared when operating your drone.
What should I do if my drone loses GPS signal?
If GPS signal is lost, immediately switch to manual mode and attempt to fly the drone back to a safe location. Be prepared to use the “return-to-home” function if available.
Where can I find information on local drone regulations?
Check your local government’s aviation authority website or FAA (for the US) website for specific regulations in your area.
How do I store my drone properly?
Store your drone in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Keep it in its case or protective packaging to prevent damage.
